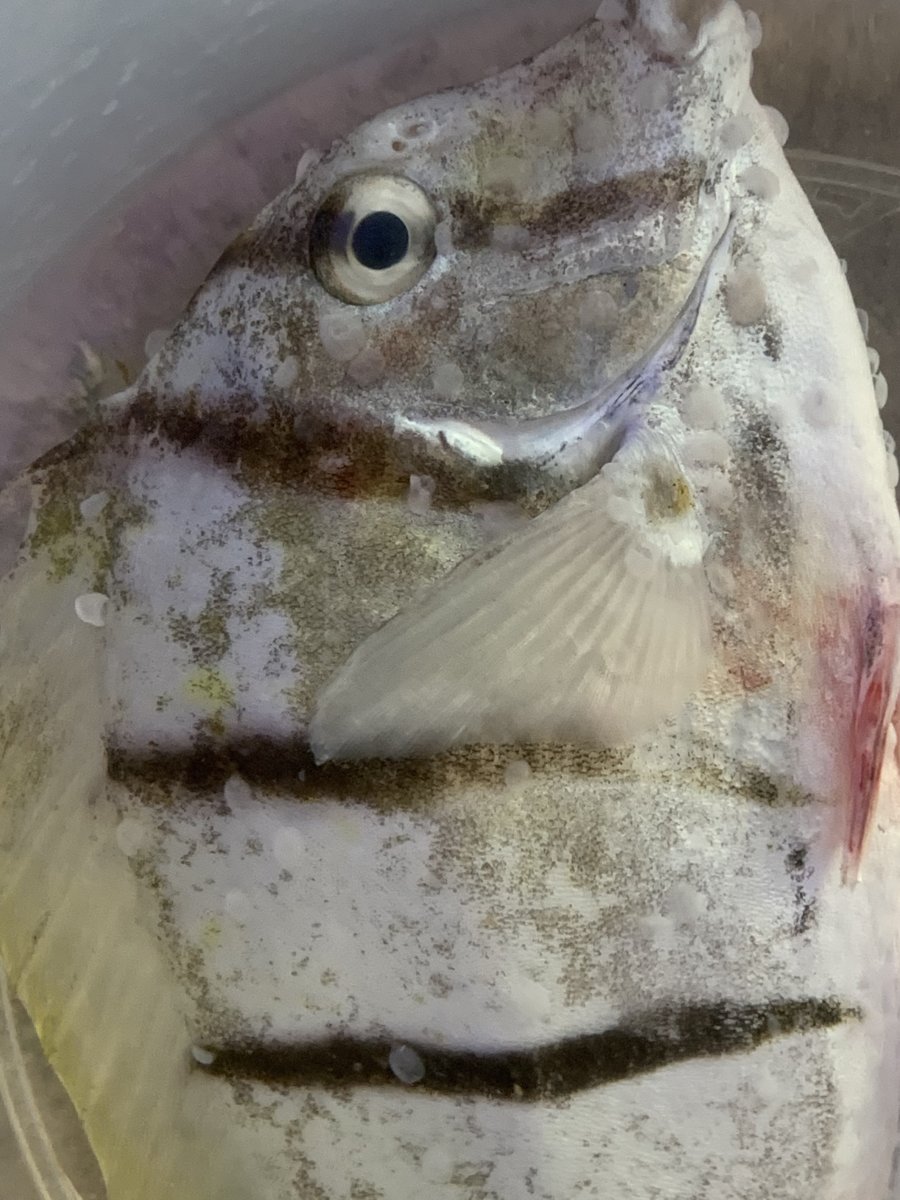
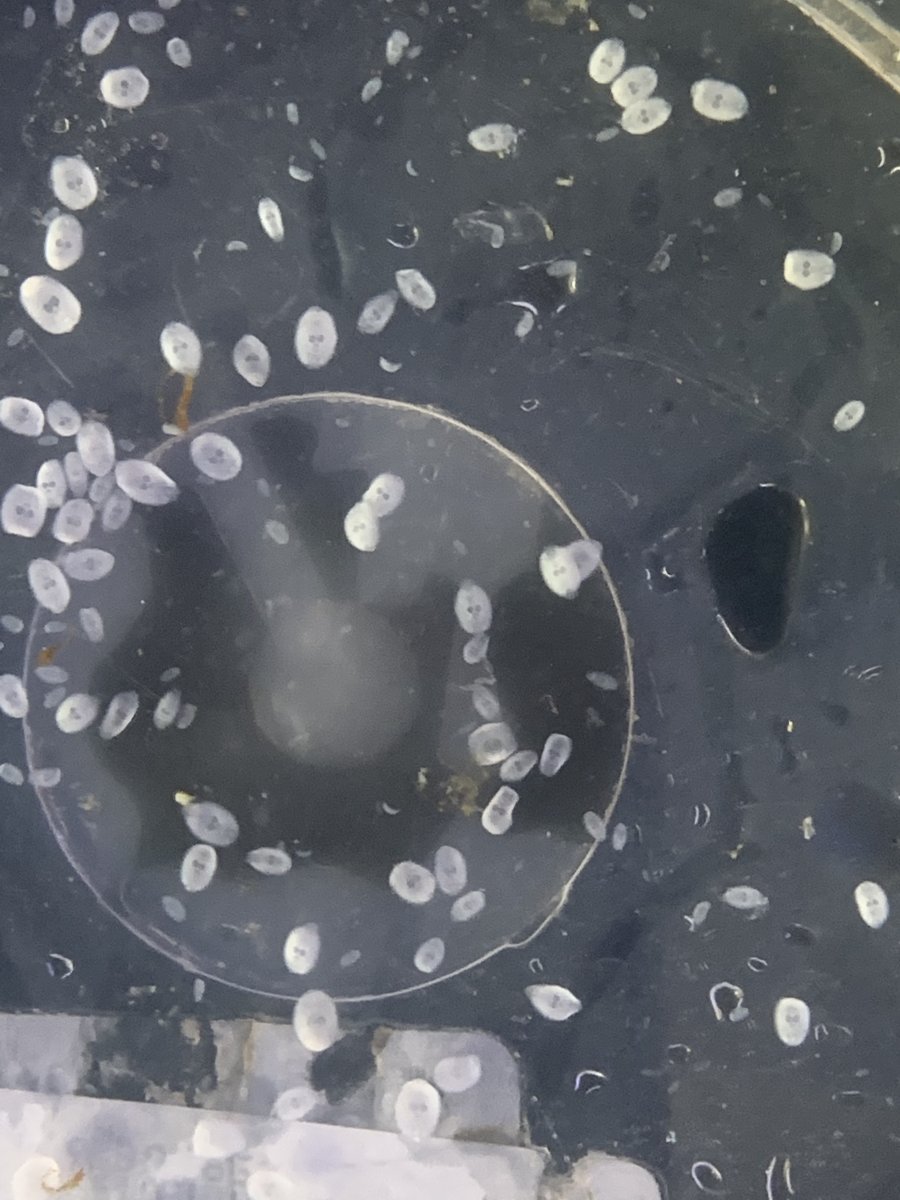
Hi, I bought a guys full system. I had issues with what I thought was bad white spot. We pulled this fish out of a 3500l system and performed a fresh water dip and found this weird parasite on it. Fish is fine in quarantine and eating. The problem is the fish I bought went into a couple of different systems and we need to treat but don’t know what this parasite is. The fish were quarantined in low salinity and cupramine and the fish looked in perfect health eating like machines before they were put into other systems but one rookie mistake on not FW dipping has put all the other fish in the systems at risk.

Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Fish parasite
- Thread starter Aquanino
- Start date
- Tagged users None
Thanks Tamberav, will do another Prazipro. Was hoping it’s just Flukes and not anything else. Have to make sure all the other fish don’t have it. None are showing signs of heavy breathing or skin abrasions/scratching but need to make 100% sure this doesn’t spread.
That is a capsalid fluke, probably Neobenedenia. It is an egg layer, so very difficult to cure with Praziquantel - the eggs are resistant to almost everything, so you need a treatment that will wait them out and kill them upon hatching. The eggs also have sticky tendrils, so they get caught on nets, etc and moved from tank to tank. For years, I tried multiple high dose prazi treatments and would typically fail. One reason for this is the egg life cycle, but the other reason is that with multiple treatments, bacterial colonies grow that actually consume the prazi faster than it can be effective (vets at Disney finally figured this out). I use 35 days of hyposalinity to treat this now. Here is an excerpt from my upcoming book on the topic:
Neobenedenia melleni (eye flukes)
These are relatively large (up to 8 mm), egg-laying worms that live on the skin or eyes of marine fishes.
Symptoms
Neobenedenia infections peak slowly; there may be no symptoms for weeks after you acquire a fish. Eventually, as the flukes multiply and grow in size, they begin to cause symptoms of disease.
The first obvious symptom may be slightly cloudy eyes, caused by the transparent fluke feeding on the eye tissue and eliciting a tissue reaction. This gives this worm the common name of “eye fluke,” although it is unknown whether these worms actually prefer to feed on eye tissue, or whether that is just where they first become apparent.
As the infection becomes more serious, the fish will “flash,” their skin color will become dull, their fins may become tattered, and they just generally get a “scruffy” look to them. Rapid breathing due to stress, possible secondary infection, and then death follow if treatment is not begun.
Diagnosis
The best means of diagnosis is to give the fish a five-minute freshwater dip. Not only does this knock back the infection by killing the adult parasites, but even a casual look at the bottom of the dip container afterwards will help to positively identify this disease. The worms turn whitish and fall to the bottom. Many aquarists mistake these for scales that were dislodged from the fish. However, looking at these “scales” under a dissecting microscope, or even a hand lens, will soon show them for what they are—dead worms.
Sometimes a fish’s history can help diagnosis at least the potential for this disease. Angelfishes and butterflyfishes are especially prone to Neobenedenia infections, so any of these fish that have been housed at an import facility that doesn’t prophylactically treat for trematodes stand a very good chance of being infected.
Angelfish, Pomacanthus sp. ++
Barrimundi, Lates sp. ++
Batfish, Platax sp. +++
Butterflyfish, Chaetodon sp. ++
Cichlid, Tilapia sp. +++ (when housed in seawater)
Invertebrates 0 (but may carry eggs)
Jacks, Caraganidae +++
Lionfish, Pterois sp. +
Lookdowns, Selene sp. +++
Pyramid butterflyfish, Hemitaurichthys sp. +++
Grouper family, Serranidae ++
Garden eel, Taenioconger sp. +
Remora, Echeneis sp. +
Sharks and rays, Elasmobranchs 0
Surgeonfish, Acanthurus sp. ++
Spadefish, Chaetodipterus faber +++
Aquarium hosts for Neobenedenia sp. 0=not infected, + = sometimes infected, ++=commonly infected, +++=very commonly infected (From Bullard et-al 2000 and personal obs.)
Treatment
Many people suggest using a freshwater dip as a treatment for all incoming fish. The two drawbacks to this are 1) the dips are not 100% effective (and do not harm the fluke eggs) and 2) newly acquired fish often do not stand up well to the added stress of a freshwater dip when they first arrive.
Neobenedenia eggs can take 14 to 30 days (or longer?) to hatch as motile larvae called oncomiracidium. Additionally, the eggs have sticky tendrils that attach them securely to all manner of objects in an aquarium. There is some merit to the idea of keeping a treatment tank free of substrate and siphoning the bottom regularly in order to remove some of these unhatched eggs. There have been reports that Lysmata cleaner shrimp feed on these eggs, rendering them non-viable. However, it is unlikely that in a normal aquarium, with many other food choices, that cleaner shrimp will markedly reduce their numbers.
Any successful treatment for these worms must be undertaken in stages. The first treatment kills off the adult worms (but this won’t kill the eggs), and the subsequent treatments kill off the juvenile worms after they have all hatched but before any of them have matured and begun to lay eggs of their own. Due to variables in timing, it is virtually impossible to accomplish this in only two treatments.
Whole-tank formalin baths at 166 ppm for one hour will eliminate the adult flukes from an aquarium but not the eggs. Because this type of treatment has no residual effect, the treatment may need to be repeated every two weeks for two or three more times. Experience in public aquarium exhibits has shown that this method rarely clears a tank completely of this pest.
A better alternative is a Praziquantel treatment at 4 ppm, followed by a 50% water change after 48 hours, then a second treatment 12 to 14 days later, followed by another 50% water change 48 hours later.
We noticed that multiple Praziquantel treatments on the same system, over months to years, required higher and higher doses, combined with increased frequency of the treatments in order to maintain effectiveness. Eventually, the praziquantel was simply no longer effective. One supposition was that the target parasites were building an immunity to the drug. That seemed unlikely as genetic change in multi-cellular organisms typically takes longer to happen (as opposed to drug-resistant bacteria that can develop resistance in short order). We wondered then, what could be rendering Praziquantel so ineffective on repeat doses?
Subsequent research indicates that bacterial degradation of the Praziquantel (Thomas et-al, 2016) is the process at work. Their study concluded that while Praziquantel is stable for over two weeks in sterile marine aquarium water, when dosed in working systems, it degrades below detectable limits in just nine days. A subsequent dose on the same system showed a reduction in Praziquantel in less than 48 hours. The presence or absence of fish in the system did not affect this rate of degradation. The natural bacterial population of the aquarium actually works to eliminate Praziquantel from the water.
Barrett L. Christie, a public aquarium curator, has researched a variety of treatment methods and has struck upon one that is highly effective. The treatment is relatively simple; in a quarantine system, the fish are exposed to hyposalinity (low salinity) for 35 days. Exactly how low of a salinity is the variable that needs to be controlled. Some species of fish do not tolerate lower salinities, yet if the salinity is not reduced enough, the parasite population is only reduced, not eradicated. Barrett has hit upon a workable value of 17 parts per thousand, a bit less than half the salinity of normal seawater (this equates to a specific gravity of around 1.013). Obviously, most invertebrates cannot be present during this sort of treatment. Sharks and some rays cannot tolerate it either. Assuming the fish are healthy in all other respects, you begin this treatment by lowering the salinity to the target value over 24 to 48 hours. During the low salinity treatment, water quality must be monitored closely, especially pH. Be aware that some other diseases, notably Uronema and Amyloodinium thrive at lower salinities. Luckily, another common scourge, marine ich, Cryptocaryon irritans, is also inhibited by low salinity. After 35 days, the salinity is gradually raised back to normal. It is imperative to perform this change back to normal seawater very slowly. While marine fish tolerate a drop in salinity very well, their kidneys have more difficulty adjusting as the salinity is raised. Never return fish to normal salinity faster than 72 hours, and don’t make large changes at one time.
Jay
Neobenedenia melleni (eye flukes)
These are relatively large (up to 8 mm), egg-laying worms that live on the skin or eyes of marine fishes.
Symptoms
Neobenedenia infections peak slowly; there may be no symptoms for weeks after you acquire a fish. Eventually, as the flukes multiply and grow in size, they begin to cause symptoms of disease.
The first obvious symptom may be slightly cloudy eyes, caused by the transparent fluke feeding on the eye tissue and eliciting a tissue reaction. This gives this worm the common name of “eye fluke,” although it is unknown whether these worms actually prefer to feed on eye tissue, or whether that is just where they first become apparent.
As the infection becomes more serious, the fish will “flash,” their skin color will become dull, their fins may become tattered, and they just generally get a “scruffy” look to them. Rapid breathing due to stress, possible secondary infection, and then death follow if treatment is not begun.
Diagnosis
The best means of diagnosis is to give the fish a five-minute freshwater dip. Not only does this knock back the infection by killing the adult parasites, but even a casual look at the bottom of the dip container afterwards will help to positively identify this disease. The worms turn whitish and fall to the bottom. Many aquarists mistake these for scales that were dislodged from the fish. However, looking at these “scales” under a dissecting microscope, or even a hand lens, will soon show them for what they are—dead worms.
Sometimes a fish’s history can help diagnosis at least the potential for this disease. Angelfishes and butterflyfishes are especially prone to Neobenedenia infections, so any of these fish that have been housed at an import facility that doesn’t prophylactically treat for trematodes stand a very good chance of being infected.
Angelfish, Pomacanthus sp. ++
Barrimundi, Lates sp. ++
Batfish, Platax sp. +++
Butterflyfish, Chaetodon sp. ++
Cichlid, Tilapia sp. +++ (when housed in seawater)
Invertebrates 0 (but may carry eggs)
Jacks, Caraganidae +++
Lionfish, Pterois sp. +
Lookdowns, Selene sp. +++
Pyramid butterflyfish, Hemitaurichthys sp. +++
Grouper family, Serranidae ++
Garden eel, Taenioconger sp. +
Remora, Echeneis sp. +
Sharks and rays, Elasmobranchs 0
Surgeonfish, Acanthurus sp. ++
Spadefish, Chaetodipterus faber +++
Aquarium hosts for Neobenedenia sp. 0=not infected, + = sometimes infected, ++=commonly infected, +++=very commonly infected (From Bullard et-al 2000 and personal obs.)
Treatment
Many people suggest using a freshwater dip as a treatment for all incoming fish. The two drawbacks to this are 1) the dips are not 100% effective (and do not harm the fluke eggs) and 2) newly acquired fish often do not stand up well to the added stress of a freshwater dip when they first arrive.
Neobenedenia eggs can take 14 to 30 days (or longer?) to hatch as motile larvae called oncomiracidium. Additionally, the eggs have sticky tendrils that attach them securely to all manner of objects in an aquarium. There is some merit to the idea of keeping a treatment tank free of substrate and siphoning the bottom regularly in order to remove some of these unhatched eggs. There have been reports that Lysmata cleaner shrimp feed on these eggs, rendering them non-viable. However, it is unlikely that in a normal aquarium, with many other food choices, that cleaner shrimp will markedly reduce their numbers.
Any successful treatment for these worms must be undertaken in stages. The first treatment kills off the adult worms (but this won’t kill the eggs), and the subsequent treatments kill off the juvenile worms after they have all hatched but before any of them have matured and begun to lay eggs of their own. Due to variables in timing, it is virtually impossible to accomplish this in only two treatments.
Whole-tank formalin baths at 166 ppm for one hour will eliminate the adult flukes from an aquarium but not the eggs. Because this type of treatment has no residual effect, the treatment may need to be repeated every two weeks for two or three more times. Experience in public aquarium exhibits has shown that this method rarely clears a tank completely of this pest.
A better alternative is a Praziquantel treatment at 4 ppm, followed by a 50% water change after 48 hours, then a second treatment 12 to 14 days later, followed by another 50% water change 48 hours later.
We noticed that multiple Praziquantel treatments on the same system, over months to years, required higher and higher doses, combined with increased frequency of the treatments in order to maintain effectiveness. Eventually, the praziquantel was simply no longer effective. One supposition was that the target parasites were building an immunity to the drug. That seemed unlikely as genetic change in multi-cellular organisms typically takes longer to happen (as opposed to drug-resistant bacteria that can develop resistance in short order). We wondered then, what could be rendering Praziquantel so ineffective on repeat doses?
Subsequent research indicates that bacterial degradation of the Praziquantel (Thomas et-al, 2016) is the process at work. Their study concluded that while Praziquantel is stable for over two weeks in sterile marine aquarium water, when dosed in working systems, it degrades below detectable limits in just nine days. A subsequent dose on the same system showed a reduction in Praziquantel in less than 48 hours. The presence or absence of fish in the system did not affect this rate of degradation. The natural bacterial population of the aquarium actually works to eliminate Praziquantel from the water.
Barrett L. Christie, a public aquarium curator, has researched a variety of treatment methods and has struck upon one that is highly effective. The treatment is relatively simple; in a quarantine system, the fish are exposed to hyposalinity (low salinity) for 35 days. Exactly how low of a salinity is the variable that needs to be controlled. Some species of fish do not tolerate lower salinities, yet if the salinity is not reduced enough, the parasite population is only reduced, not eradicated. Barrett has hit upon a workable value of 17 parts per thousand, a bit less than half the salinity of normal seawater (this equates to a specific gravity of around 1.013). Obviously, most invertebrates cannot be present during this sort of treatment. Sharks and some rays cannot tolerate it either. Assuming the fish are healthy in all other respects, you begin this treatment by lowering the salinity to the target value over 24 to 48 hours. During the low salinity treatment, water quality must be monitored closely, especially pH. Be aware that some other diseases, notably Uronema and Amyloodinium thrive at lower salinities. Luckily, another common scourge, marine ich, Cryptocaryon irritans, is also inhibited by low salinity. After 35 days, the salinity is gradually raised back to normal. It is imperative to perform this change back to normal seawater very slowly. While marine fish tolerate a drop in salinity very well, their kidneys have more difficulty adjusting as the salinity is raised. Never return fish to normal salinity faster than 72 hours, and don’t make large changes at one time.
Jay
vetteguy53081
Well known Member and monster tank lover
View Badges
Partner Member 2024
Excellence Award
Reef Tank 365
RGB
Article Contributor
Tampa Bay Reef Keepers
West Palm Beach Reefer
Hospitality Award
Ocala Reef Club Member
305 Reef Club
Wisco Reefers
Midwest Reefer
Fish Medic
MAC of SW Florida
Rock Pool Reef Keepers
R2R Secret Santa 2023
My Tank Thread
My Aquarium Showcase
Infestation is not the word !! The one with the stem appears to be ich protoan.
Wow !!
Wow !!
Thanks Jay, that is really good information. Well super stressed now as most of my fish have been with me for more than 8 years and this fish has been In the 1200l and 3500l. I have dipped my Sohal and black tang but there is nothing on them. I will keep monitoring and treating accordingly.
Hi, just an update. I did two doses of Prazipro. Worked great. Fresh water dipped a couple of fish and they are all clean and everyone is doing well. I did add about 20 cleaner shrimps to the main display and the first few days the fish were going to get cleaned constantly but that has stopped now but I can’t confirm if the shrimps had an effect as well.
Hi, just an update. I did two doses of Prazipro. Worked great. Fresh water dipped a couple of fish and they are all clean and everyone is doing well. I did add about 20 cleaner shrimps to the main display and the first few days the fish were going to get cleaned constantly but that has stopped now but I can’t confirm if the shrimps had an effect as well.
Apparently, the biggest benefit from cleaner shrimp is that they eat the Neobenedenia eggs. It takes a lot of them to make a dent in the population, but then, you added 20 when most people would have bought 2 (grin).
Jay
Similar threads
- Replies
- 12
- Views
- 273
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 154
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 198
- Replies
- 97
- Views
- 2,142















